-
Category
Craniomaxillofacial Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Spine Surgery
Orthopedic Implants
Hip Surgery
Knee Surgery
Pectus Excavatum
Bone Graft
Disinfectants
Healthcare
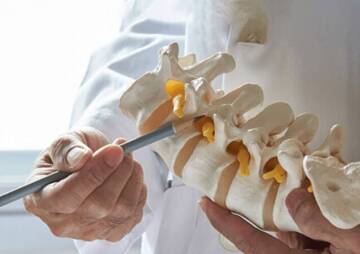
Types of intervertebral disc replacement methods
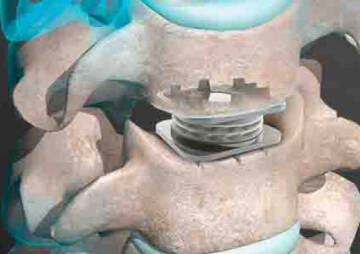
Most people over the age of 40 have some degree of disc herniation. Disk replacement surgery is one option to correct this problem.
Almost all people over the age of 40 suffer from some form of disc herniation (degenerative disc disease). It is a disease in which the intervertebral discs become weakened, causing pain, reduced range of motion, and reduced quality of life.
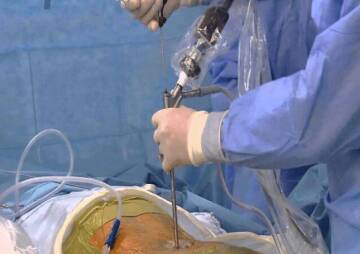
Artificial disc replacement (intervertebral disc arthroplasty) and complete disc replacement (spinal arthroplasty) is a type of spine surgery to replace a damaged disc with an artificial joint. In this operation, the spine surgeon removes the problem disk and inserts a metal or plastic prosthesis between the vertebrae.
Artificial disc replacement is a great option for spinal surgery for certain patients. Artificial discs allow the spine to be much more mobile than is achieved with spinal fusion surgery.
There are several types of disc replacement surgery. Stay with us until the end of this article to answer all your questions about this type of surgery.
The role of discs in the spine
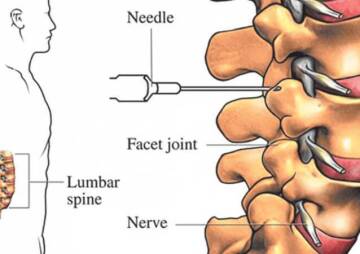
The spine is a set of bones on top of each other in the neck and back. By moving them on each other, it is possible to bend and rotate the waist and neck. Among most pairs of vertebral bones is a disc.
These intervertebral discs play three important roles in the body.
- Shock and pressure absorption
Discs have cushioning properties that relieve the pressure of heavy activity from the spine.

2. Preserve the space between the vertebrae
The discs not only prevent bone breakage, but also maintain a natural and physiological distance between the vertebrae so that nerve fibers can pass freely through the spinal canal without any pressure or stimulation.
3. Ability to move
If the vertebrae of the spine cannot move, the spine will be strong and stable. The discs allow flexibility and movement of the nut and will provide full range of motion back and forth.
Why are natural disks replaced with artificial disks?
Intervertebral discs can be damaged for a variety of reasons. In this case, one of the best solutions to reduce the pain caused by this problem is to replace the disc.
Artificial disc replacement is recommended for people with the following diseases.
Degenerative disc disease is a type of natural wear and tear on the intervertebral discs caused by aging, movement, and physical stress.

A disc herniation is a type of intervertebral disc that protrudes from its normal space in the spine. As a result of this protrusion, pressure is applied to the spinal canal and the nerve in the back or neck is pressed. These pressures will cause chronic back pain or neck pain.
Spinal stenosis, which is called narrowing of the spinal canal. This is a space channel for the passage of nerve fibers, the narrowing of which will cause pain.
How to replace a disk?
When the decayed disc is removed, the top and bottom plates of the synthetic disc are glued to the nut. Once these plates are in place, the centerpiece, known as the core, is inserted between the plates. This central nucleus allows the spine to bend and make it flexible so that the spine will move as if it were healthy.

Types of disk replacement methods
Disk replacement is divided into several categories according to the type of surgery:
Cervical disc replacement
In this procedure, the surgeon makes a three- to four-centimeter incision in the front of the neck to access the cervical spine. It then removes the damaged disc and smoothes the surface of the vertebrae. The metal plates are inserted into the nuts and then screwed on. The surgeon then inserts a polymer core between them to replace the disc. These metal plates are eventually bonded to the beads.
Prodisc-C, Mobi-C cervical disc, Medtronic Prestige LP and M6-C are common types of artificial cervical discs.

Lumbar disc replacement
For this replacement procedure, the surgeon makes a 7 to 10 cm incision in the abdomen and around the navel. To access the spine, the intestines, arteries, and arteries are pushed aside and the polymer plates and nucleus are inserted.
Artificial lumbar discs include CHARIT É Artificial Disc, Prodisc-L and ACTIV-L.

Lateral total lumbar disc replacement
In this method, access to the spine is possible from the back instead of the abdomen. This will reduce the risk of abdominal injury and shorter hospital stays and recovery.
Hybrid surgery
If two adjacent discs are also a problem, the surgeon usually uses a combination method. In this model, one disc is replaced and the other is welded next to it. In fact, this method involves fusion and replacement at the same time.

Who are the candidates for disk replacement?
Many, but not all, people with back problems are candidates for disc replacement. The main cause for artificial disc replacement is degenerative disc disease, which may or may not be associated with radicular pain. This pain is caused by compression or inflammation of the nerves in the spine.

In people who are candidates for artificial disc replacement, neck or back pain is usually so severe that they are unable to work or exercise.
In general, most people should have chronic neck or back pain for at least six months that has not been affected by non-surgical methods. This means that after heat treatment, physiotherapy, oral analgesics or corticosteroids, if the person still has unbearable pain, he will be a candidate for disc replacement.
How successful is disc replacement surgery?
This treatment can be done at almost any age, but it works best in young and middle-aged people (18 to 60 years old). The important point is that the vertebrae around the artificial disc must be healthy enough to support it. For this reason, people who have had unsuccessful spinal surgery in the past, those with spinal osteoporosis, vertebral compression, or ankylosing spondylitis will not be candidates for artificial disc replacement and the success rate of this type of surgery. In them it is almost zero.

Benefits of Artificial Disk Replacement
Various studies on vertebral disc replacement have shown that this procedure:
- Reduces or eliminates chronic neck or back pain.
- After the operation, unlike fusion surgery, the spine will move easily.
- Improves quality of life.
- Eliminates the need for bone grafts.
- Recovery from this procedure is faster than fusion surgery.
- Artificial disks last more than 70 years.
Risks of artificial disk replacement
As with all surgeries, there are potential risks to disc replacement. The likelihood of these problems depends on various factors, including the patient's general health. These risks can be categorized into several groups.
General risks of disk replacement
- Rupture of the dura (protective sheath around the spinal nerves) which can cause spinal fluid leakage.
- Infection
- Postoperative bleeding
- Nerve damage that leads to weakness or numbness.
- Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism)
- Damage or replacement of the prosthesis.

Risks in cervical disc replacement surgery
- Difficulty swallowing temporarily
- Temporary loss of sound
Risks in lumbar disc replacement surgery
- Damage to the small or large intestine
- Injury to the ureter (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder)
- Temporary reduction of bowel movements
- Problems with ejaculation in men. A condition in which a man's semen goes to the bladder instead of coming out through the penis.
Long-term effects of disk replacement
- Problems in adjacent vertebrae
- Prosthesis wear
- Lack of pain relief (or worsening of symptoms)
- Surgical failure that may require further surgery or another type of surgery such as spinal fusion.

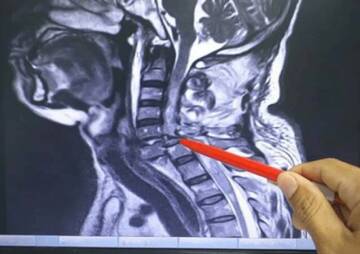
Can I have an MRI after a disc replacement?
Whether or not the MRI results are correct after spinal disc replacement is directly related to the type and type of prosthesis used. .
If you intend to replace the artificial disk, make sure that:
- Artificial disc replacement is not suitable for all types of spine pain and any type of disease.
- Your doctor will not recommend this type of surgery unless the symptoms are severe.
- Choosing an experienced surgeon is essential to achieve the best results
- The cost of replacing a lumbar and neck disc varies depending on the type of artificial disc used, the type of hospital, the doctor's salary, and the geographic area. The total cost includes the cost of surgeons, anesthesiologists, prosthetics and facilities. In the United States, for example, if health insurance does not cover the cost of disc replacement surgery, the amount will vary from $ 30,000 to $ 50,000 to replace one to two discs.