-
Category
Craniomaxillofacial Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Spine Surgery
Orthopedic Implants
Hip Surgery
Knee Surgery
Pectus Excavatum
Bone Graft
Disinfectants
Healthcare
Cervical Spondylosis, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Neck pain can have many causes. Cervical spondylosis often causes pain and stiffness in the neck. Familiarity with the symptoms, to prevent cervical spondylosis pain Do not miss this article.
Neck pain can have many causes. But in many cases, the pain is due to old age. Like other bones in the body, the bones of the spine degenerate with age and cause various problems in the spine's structure. If this injury occurs in the neck, it is called cervical spondylosis.
Cervical spondylosis is very common. More than 85% of people over the age of 60 have the disease. This condition often causes pain and stiffness in the neck. Familiarity with the symptoms, methods of prevention, treatment, and prevention of the increase of this disease will increase people's quality of life.

Neck spondylosis and the site of the pain
The spine comprises 24 bones called vertebrae, which form a protective canal for the spinal cord. Among these 24 vertebrae, seven vertebrae that start at the skull base include the neck and are known as the cervical spine. Spondylosis is a neck pain that occurs in this part of the spine.

What are the most important causes of osteoarthritis of the neck?
Cervical spondylosis is caused by age-related changes in the bone tissue of the spine. These changes are perfectly normal and occur in all older people. About half of middle-aged and older people have degenerated bones in the spine, but have no annoying or painful symptoms. Some of the most important causes of cervical spondylosis are:
Disk Degeneration
As the intervertebral discs in the spine age, they lose their thickness and become deformed. In some cases, the water inside them dries out, and its thickness decreases. In this case, the discs and vertebrae's lateral pressure gradually increases, causing destruction and spondylosis of the neck.

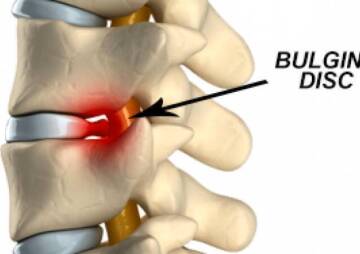
Disk herniation
Natural ageing can cause the outer part of the spinal disc to crack. In this condition, the disc's inner part is removed, which is called a herniated disc or hernia. The hernia puts pressure on nearby tissues or the spinal nerve, and this pressure is the leading cause of pain, tingling or numbness.

Osteophyte
The smooth and slippery articular cartilage covers and protects the joints. This cartilage will also wear out gradually with age. If the cartilage worn out completely, the bones may wear on against each other. To make up the lost cartilage, a new bone is made in place of the joints to support the vertebrae. Over time, this bone grows so large that it is called a bone spur. Overgrowth of bone spurs and may narrow the passage of nerves and spinal cord and cause Cervical Spondylosis.

Neck injuries
Injuries to the neck due to accidents, such as falls or accidents, can lead to faster destruction of the vertebrae and premature ageing, resulting in the neck's osteoarthritis.

Ligament stiffness
Ligaments are strong cords that connect the bones of your spinal cord. If the ligaments tighten over time, they will affect your neck's movement, causing pain and cervical spondylosis.
Excessive pressure on the neck
Some jobs or sports involve repetitive, heavy neck movements that put extra strain on the spine, resulting in premature wear and tear and osteoarthritis of the neck.

Who is most at risk for cervical spondylosis?
Older people are more likely to get cervical spondylosis because it is associated with old age. But other people are also prone to disease. Including :
- Those who smoke.
- Depressed and anxious people
- People with a genetic background
- People with a history of previous injuries from an accident
- Building painters who look up at your head for hours every day, or plumbers and floor installers who hold their heads down for long periods.

- People who put their head in an awkward position for a long time, such as staring at a computer screen for a long time.
- Construction workers doing heavy work.
- Bus or truck drivers who are exposed to vibration for a long time.
Recognize the symptoms of cervical spondylosis
In most people, cervical spondylosis has no symptoms, but it usually presents as neck pain and stiffness if symptoms do occur. This pain may be mild or severe.
Sometimes the pain is made worse by looking up, looking straight ahead, or doing activities that require the neck to be in a position for a long time, such as driving or reading a book. These pains improve with rest or lying down.

But other symptoms can indicate osteoarthritis of the neck. Such as headache, dizziness, hearing the sound of splitting when turning, and muscle spasms in the neck and shoulders.
A common symptom of cervical spondylosis is pain around the shoulder blade. Somebodies complain about pain in the arm and fingers. This pain may be exacerbated when standing, sitting, sneezing, coughing, and bending the neck backwards.
In some cases, cervical spondylosis leads to narrowing of the spinal cord and nerve roots. In this case, it will be accompanied by symptoms such as numbness and weakness in the arms, hands and fingers, difficulty walking, loss of balance, lack of control over urination and defecation, or weakness in the arms or legs.
Methods of diagnosis of cervical spondylosis by physicians
When a person sees an orthopedist with neck pain, in the first stage, after the medical history, the doctor performs clinical examinations on the shoulders, neck, arms and legs. He checks the strength of the arms and fingers, the strength of touch, reflexes, blood flow, gait balance, and more. He then compiles a history of pain.

In the second stage, the doctor may order diagnostic tests to ensure the patient has cervical spondylosis. These tests include the following.
- X-rays show the bones of the neck, their alignment, bone loss and bone spurs.
- Computed tomography (CT) scans provide more detail than X-rays. This scan can help you see your spinal cord and bone spurs better.

- MRI images show soft tissues details such as cartilage, nerve roots, muscles, spinal cord, and discs. This test can show compression of the spine or herniated disc more clearly than X-rays. MRI electromyography can help identify the source and location of the pain.
- Other tests may include myelograms (CT scans) or electromyograms (nerve function tests). These tests provide more details about the effects of cervical spondylosis on your nerves.
Treatment of cervical spondylosis
When a physician diagnoses cervical spondylosis, patients have different treatments depending on the severity of the disease.
Non-surgical treatment
In most cases, treatment for cervical spondylosis is non-surgical.
In the first stage of treatment, the doctor prescribes several medications to relieve both pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are often prescribed with acetaminophen to relieve pain. Medications such as cyclobenzaprine or carisoprodol use to treat painful muscle spasms.

Physiotherapy is a non-surgical treatment option that doctors recommend. Specific exercises can help relieve pain as well as strengthen and stretch weak muscles.
Home treatments for cervical spondylosis include the use of neck guards that restrict your neck movements and massage, hot and cold compresses to relieve pain.

Steroid injections are also one way to reduce inflammation and pain in the neck, which is very rare and is recommended by doctors in certain conditions.

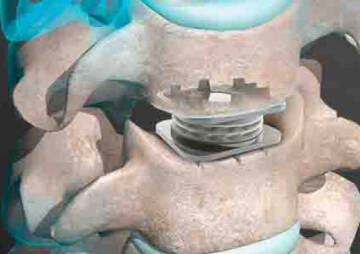
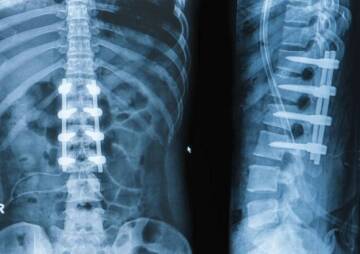
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is not usually used for cervical spondylosis unless the condition is particular. For example, when the spinal cord and nerves are under pressure and the patient has progressive neurological symptoms such as arm weakness and anesthesia.

Surgery may also be recommended if you have severe pain that does not resolve with non-surgical treatment. However, some patients with severe neck pain will not be candidates for surgery, which may be due to the widespread nature of their osteoarthritis, other medical problems, or other causes for their pain, such as fibromyalgia.
How can cervical spondylosis be prevented?
Cervical spondylosis, which is caused by aging, may not be prevented, but you will reduce your risk of developing it if you follow some principles.
- Try to be in the best physical position when standing, sitting, and sleeping
- Have a regular physical activity.
- When exercising, always use appropriate sports equipment under the supervision of a trainer.
- Beware of blows to your neck.

Facts About Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is more common in the elderly; however, there are no symptoms in many cases, and the person will never notice the disease.
Patients with cervical spondylosis usually do not have a disability and do not need severe treatment, and if pain occurs, it can be treated with physiotherapy and some medications. But sometimes, changes in the spine can compress the spinal cord or the nerve roots attached to it, in which case the person will suffer from numbness and imbalance and similar problems. In these cases, doctors use surgical methods to solve the patient's problem, which is very rare.