-
Category
Craniomaxillofacial Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Spine Surgery
Orthopedic Implants
Hip Surgery
Knee Surgery
Pectus Excavatum
Bone Graft
Disinfectants
Healthcare
Cranioplasty and its meaning
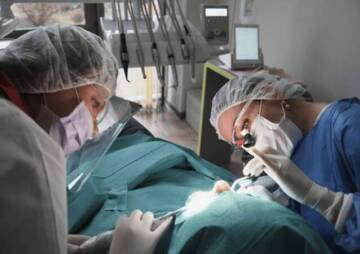
A craniotomy is a common type of surgery performed to remove a brain tumor, remove a blood clot, and control bleeding from a weak blood vessel.
Head reshaping or skull reshaping can be a congenital problem due to previous surgery and trauma to the head. But it is necessary to solve this problem and cranioplasty is the cure for this problem. Cranioplasty has cosmetic and protective benefits for patients with cranial defects. But what does cranioplasty mean and how is it done?
The concept of cranioplasty
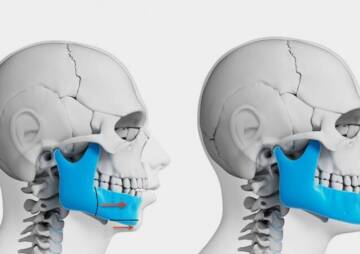
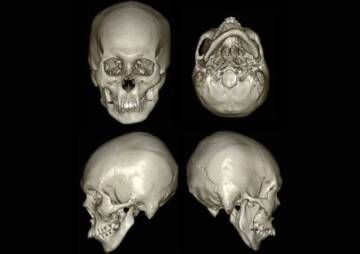
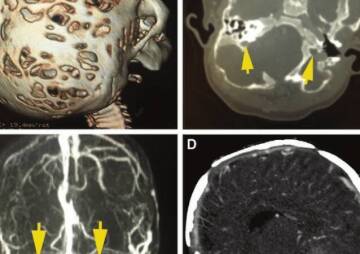
Cranioplasty (CPL) is a secondary surgical procedure performed to restore a skull defect after a previous operation by removing the skull flap. In other words, cranioplasty means, a type of head plastic surgery that is performed to correct a skull bone defect. Skull bone defects can be due to a head injury, previous head surgery, or congenital defects. Cranioplasty surgery eliminates this problem and restores the appearance of the skull to a normal shape.
_1.jpg)
Difference between craniotomy, craniectomy, and cranioplasty meaning
A craniotomy is a common type of surgery performed to remove a brain tumor, remove a blood clot (hematoma), and control bleeding from a weak blood vessel (brain aneurysm). It can also be used to repair arterial-venous abnormalities (abnormal connections to blood vessels), drain brain abscesses, relieves intracranial pressure, and perform brain biopsies.
Craniectomy is similar to craniotomy, except that the skull bone does not fall into place immediately after the craniectomy.
But cranioplasty is a type of corrective surgery that is performed after craniotomy or craniectomy to return the skull to its normal shape.

Method of performing cranioplasty surgery
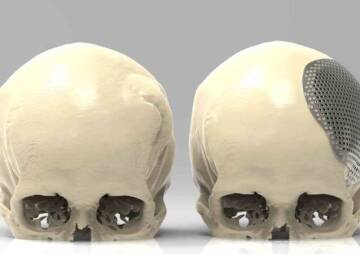
Cranioplasty is one of the oldest methods of cranial bone repair. The first primitive cranioplasty surgery dates back to 7,000 years ago. Today, over time, this type of surgery has undergone many changes and is performed in different ways. The most common is lifting the scalp and repairing it with a piece of the original skull or a custom contour graft. Custom contours come in three different modes.
- In the form of a titanium plate or mesh
- Artificial bone in liquid form
- A solid biomaterial that is a prefabricated bone that matches the exact contour and shape of the skull.
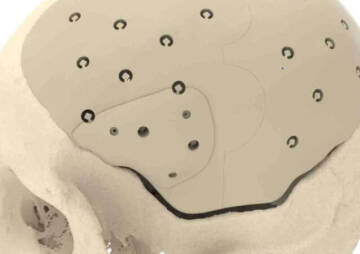
In the traditional cranioplasty procedure, all five layers of the scalp are removed to place a bone or an artificial implant in the right place on the skull. In this procedure, the surgeon examines the skull bone after cutting the scalp. If the skull bone is healthy, the same bone will be deformed and put in the right place. Then it is held in place with the help of titanium plates and screws. But if the bone is not healthy, artificial parts or even bone from other parts of the body, such as the pelvis or ribs, are used.

A newer method of cranioplasty surgery called "cranial cranioplasty" is safer and less invasive. In this procedure, the surgeon removes only the top three layers of the scalp and places a bone or implant between the remaining layers of the scalp to protect the brain.
Why do doctors recommend cranioplasty surgery?
Doctors recommend cranioplasty for a variety of reasons.
When cranial defects in the brain are damaged. For example, as a result of an accident, it is necessary to remove part of the skull bone to reduce pressure on the brain, or after surgery to remove a brain tumor, a part of the skull is down.
- When cranial correction improves nerve function in the patient.
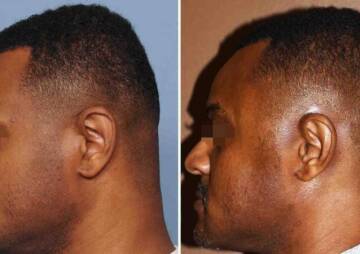
- When the shape and appearance of the deformity (asymmetrical and irregular shape) of the skull reshaping adversely affects the appearance and self-confidence of the patient.
When injuries and headaches from previous surgery bother the patient.

Risks of cranioplasty surgery
All surgeries have some kind of risk. Cranioplasty has special benefits for the beauty and function of the brain and is a simple surgical procedure, but usually has a relatively high-risk rate of about 10 to 50 percent. The most common risks of this reconstructive surgery are:
Hydrocephalus is the most common complication of cranioplasty. One study showed that the probability of its occurrence is 34.9%. (5)
The risk of infection that requires antibiotic treatment is about 6.4%
Postoperative blood clot (Hematoma) that needs to be drained is about 6.4%
- Seizures with a probability of 9.9%
- Headache with a probability of 9.9%
- Stroke
- Blood clots in the legs that in some cases go to the lungs and cause pulmonary embolism.
- Complications such as pneumonia, heart attack, and urinary tract infections that are not directly related to cranioplasty surgery.
As you read, cranioplasty is not a surgery without complications, but in some cases it is necessary. If this surgery is done correctly at the right time and in the right way, it will bring good results.