-
Category
Craniomaxillofacial Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Spine Surgery
Orthopedic Implants
Hip Surgery
Knee Surgery
Pectus Excavatum
Bone Graft
Disinfectants
Healthcare
How long do metal implants last in the body? The question you should ask before implant placement
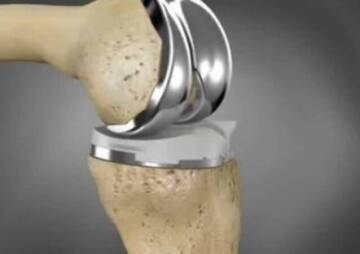
Titanium implants in the body can last up to 20 years without changing their quality. But does the material of the implant affect its durability? What is the body's immune response to implants? Read this article.
Medical science utilizes a variety of materials to repair or replace damaged tissue. For a long time, the body's reaction to implants and metal implants' durability has been the most critical issue regarding implant placement. Necessary raw materials may be obtained from humans or other living organisms. Generally, suppose biological materials are used to repair a part of the body. In that case, they are transplanted, and when artificial materials are used to replace tissues, they are classified as implants. Because implants have great potential to harm humans and even animals, they are subject to strict FDA regulations. The implant is a Class 3 medical device that must be manufactured and used in compliance with all FDA regulations at this level. Any non-medical use of the implant is strictly prohibited.
When each titanium implant enters the body, it can last up to 20 years. Dental titanium and dental implants can stay in place for even longer than 20 years without any change in quality. However, does the material of the implant affect its lifespan? What is the body's immune response to implants? Do implants have an expiration date? You will get the answers to all your questions by the end of this article.
Orthopedic Implants, Treatment for Moving the Joints of the Body
Correctly yet flexible metals are utilized in this medical industry. These properties have led to their widespread use in structural applications. Metals and alloys can be divided into ferrous groups such as steel and cast iron, and non-ferrous. Non-ferrous metals and alloys are the most commercially important groups. The most widely used include pure elements and alloys of aluminum, copper, silver, titanium, zinc, and cobalt. These metals are used as biomaterials due to their excellent thermal, conductivity, and mechanical properties. Such biomaterials are used in the construction of structures and implants in the body. Implants replace the lost biological system of a diseased body or are used to restore the shape of a part of the body. It can be said that biomaterials help to improve the quality of life and increase longevity. In general, metal biological materials are used to withstand loads on parts of the body that have lost their resistance, especially in the elderly. In the last decade, the use of bio-implants or biological implants to meet the elderly human population's demands has overgrown. Today, different parts of our body can be rejuvenated using biomaterials and metal implants' durability in the body. Orthopedic implants, the backbone and used in cranial, shoulder, knee, hip, elbow, corner, orthodontic surgeries, and orthodontic structures have evolved using biological materials.
Application of Implants in Different Parts of the Body
In most cases, the surgeon must injure the tissue before implanting any implant. Another essential step in the implantation process is to remove as much of the patient's damaged tissue as possible. The success of the whole operation, the durability of metal implants in the body, and the receipt of good response (response) depend on the type and degree of tissue response called implants' biocompatibility. Biocompatibility requires mechanical, chemical, and surface compatibility. The response of body tissue to the damage caused by implant placement may vary depending on the site, species, contamination, and other conditions.
However, the inflammation and the cellular response to the wound are the same in all cases. The body's response to any foreign object is a protective defense mechanism that can detect and react to allergens or toxins, warning the physician. Biomedical implants are now widely used in orthopedics, dental implants, breast implants, vascular transplants, cardiology, ophthalmic lenses, and smart drug injection pumps.
Reaction and durability of metal implants in the body are not familiar to all medical implants. Sometimes implants do not coordinate with living tissue, and the fibrous capsule shows different responses. For example, contraction of the breast implant capsules causes the implant to shrink while the capsule response of implant injection pumps is entirely different. Sometimes, the body's inappropriate response interferes with the drug's molecular distribution or leads to failure.
What are the Materials Metal Implants?
The most common metals and alloys used in implants include stainless steel, cobalt-chromium alloy, titanium, and nickel-titanium alloy (nitinol)—material friendly metal engineered materials which are designed to provide built-in support of biological tissue. Orthopedics, dentistry, followed by the heart (pacemaker and artificial heart valve), and vascular neoplants (aneurysm clips) are the most widely used implants. In contrast, biomaterials are natural biomaterials derived from plants or animals. Natural biomaterials are used to strengthen, replace, or repair tissues and organs in the body. Alternative tissues are usually taken from pigs because they are most compatible and similar to human body tissues.
List of Biomaterials Widely Used in Implant Making
Titanium alloys made from non-toxic, non-allergenic elements, and stainless steels (nickel-free and Co-Cr alloys) are being developed. Examples of biological materials are:
- Alumina
- Zirconia
- Titanium
- Niobium
- Carbon
Examples of synthetic components made from biomaterials are:
- Joint replacement
- Bone plate
- Intraocular lenses (IOLs)
- Bone cement
- Artificial ligaments and tendons
- Dental fixation dental implants
- Blood vessel prosthesis
- Heart valves
The Durability of Metal Implants in the Body
Substances implanted under the skin activate the body's immune system and cause the body to react. This reaction includes protein uptake on the implant surface, infiltration of inflammatory cells, macrophage fusion into the body's external giant cells, and fibroblast activation. Such a series of events may affect the durability of metal implants in the body, especially subcutaneous implants' function.
Implants such as inhibiting the release of drugs from a specific part of the body or various medical device failures are in this group. The body's response to implants is so complex that it is impossible to list them completely. Use anti-fibrotic drugs to prevent or minimize fibrosis. Combination approaches such as hydrophilic coatings, which reduce protein uptake along with dexamethasone delivery, are the most effective way to reduce the body's adverse reaction to implants.
Symptoms of rejection of bio-implants
Failure rates vary for different implants, and no specific percentage can be determined. Nowadays, various implants are produced with complex tasks and purposes, each of which is located in other parts of the body. Depending on their location and the task at hand, each of them will react differently in planting. The durability of metal implants in the body depends on these reactions. Implants may rule out implantation for various reasons, including overheating of the bone during implant placement, contamination of the implant surface, systematic problems with other organs, and implant self-immunity. Pain, itching or burning, local inflammation are common symptoms of rejection or implant problems. Diabetes and smoking can increase the signs of rejection. Implants are made of synthetic materials and are naturally covered by a biofilm in the body. The biofilm range is a favorable environment for bacteria to grow. Tissue damage and detachment of the implant due to bacterial production are signs of rejection and failure of the implant.
Side effects of metal implants
The long-term presence of a combination of alloys affects the durability of metal implants in the body and cannot be without signs and side effects. The introduction of metal particles removed by wear and tear is sometimes seen in the urine. Over time, smaller particles may enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body.
Numerous studies on the use of metal implants have reported increased Cr and Co levels in the blood and urine. These two elements are among the most essential potentially toxic ions released by orthopedic implants. Implant corrosion is a common occurrence.
The amount of wear can be assessed by assessing the level of ions in red blood cells. Element CO can affect many organs and cause various symptoms such as tinnitus, dizziness, deafness, blindness, and seizures. The liver and kidneys are also the first organs to be affected by CO. The element Cr causes harmful effects on male fertility and reduces sperm production and quality. The presence of another toxin called Al in implants, and their entry into the bloodstream has been linked to neurological conditions such as memory loss, gait disturbances, and involuntary movement.
Incompatible plates and screws in the body
Metallosis is a severe blood poisoning condition caused by high levels of toxic metals in the blood. Metal allergy is one of the most acute side effects of using metal screws and fittings in the body. In cases where the implant must be attached to the bone, the surgeon inevitably uses plates and screws and fittings, which is an essential issue in rejecting the body's incompatibility with the implants. The connecting parts of some implants can cause more damage and sensitivity in the body than the primary device and ultimately carry the risk of implant rejection. Nickel and other metals that makeup screws and retaining plates regularly stimulate the immune system. For this reason, it is possible to design the artifacts in such a way that after a while, the screws and fittings can be removed from the body, and the durability of metal implants in the body can be increased.
Side effects of implant screws in the body
Researchers think that patients are not allergic to titanium but to titanium impurities, including nickel, chromium, and cadmium. A test called MELISA is performed before surgery to investigate the durability of metal implants in the body and determine if a person is allergic to titanium. In this very detailed test, a blood sample is taken and tested for titanium sensitivity.
In the early stages, low levels of titanium can only cause hives, eczema, and pain, but high and long-term titanium levels in the body cause metallosis, which can lead to bone or tissue death. Such titanium has a devastating effect on the brain, heart, eyes, and other organs.
Do implants have an expiration date?
Patients who wear metal plates, screws, plates, or prostheses are concerned about their safety and long-term effects. Surgeons consider it very important to be worried about the durability of metal implants in the body and their long-term existence. Because these substances can cause insoluble problems, it is always possible to remove an implant in the long run. However, the materials used in implants have been designed and manufactured for a long time.
Immune response to implants
When the immune system is activated in the body, it usually causes inflammation, which affects the whole body. Only a specialist can find the cause and location of the problem. There are different reactions to using an implant, sometimes with one or more of them. Side effects such as:
- General allergic reaction (skin rash)
- Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease)
- Hearing or vision disorders
- Mental state change (depression)
- Kidney dysfunction
- Thyroid disorder (neck pain, weight gain, or feeling cold)
The biomaterials used in implants reduce the inflammatory effects as much as possible. However, after each implant is used, the immune system responds. The incidence of metal allergies in men is 13% higher than in women.
Reducing the amount of wear produced by surfaces in artificial joints is likely to lead to less implant failure. Therefore, introducing new materials and efforts to create artificial surfaces with lower wear and biologically acceptable for use in this sector has accelerated.
Titanium is an excellent biological material for implantation in the body
Titanium is a biological substance. Chemical stability, mechanical behavior, and biocompatibility in body fluids and tissues are essential requirements for successfully using implant materials in fractures and bone replacement. Metals such as stainless steel and titanium are widely used for the durability of metal implants in the body. Corrosion is one of the disadvantages of orthopedic devices used as implants in the body—failure of stainless steel implant devices shows significant local deterioration. Even one of the most durable titanium, TiO2, is worn, and titanium particles are released into the body. To reduce corrosion and achieve better biocompatibility, an alloy made of stainless steel with titanium and nitrogen is used. For body surfaces, parts made of stainless steel alloy with bio-ceramic coating are used, which improves the performance and life of the surface coating.
The most important properties of titanium for compatibility with the body
Previously, gold, silver, lead, and aluminum were used in implants and implants. One of the latest findings was the use of titanium. Nowadays, after years of testing, it has been proven that of all the metal implants in the human body and for various reasons, titanium implants are the most suitable type. The main reason for using titanium is that it can last for up to 20 years. Another essential feature of this metal is that it is not eaten by the human body and is readily accepted by the body. Because it is more resistant to dangerous reactions, these are not the only advantages of titanium, and there is a long list of titanium properties. The most important properties of titanium are as follows:
- It has a low density and does not harm humans.
- It has high strength and durability.
- It is resistant to oxidation.
- It is non-magnetic and non-toxic.
- It has a low mass.
- Compared to other metals, it is less prone to allergies.
- It is rigid and comfortable with making accessories with.
Future Perspective: Titanium Implants
Titanium plays a vital role in the durability of metal implants in the body. Of course, titanium is becoming the most extensive medical engineering material. Titanium alloys are the best alternative for the hip joint due to their excellent properties. The metal acts as a biocompatible material and does not cause adverse reactions when in the body. It also works very well mechanically and shows an intelligent and treatment-responsive response against corrosion and ossification.
Titanium is non-toxic and does not cause any inflammation in the body after implantation. The high success rate of using this metal indicates the useful and unique properties of this biomaterial. Titanium is also excellent for fracture repair and bone replacement and has a perfect capacity for bone and tissue presence without the usual side effects. In orthopedics, biocompatibility is the essential part, and titanium was the highway that orthopedic medicine needed.
Side effects of titanium implants
One of the causes of implant failure can be attributed to an allergic reaction to titanium in the body. Users of titanium implants have reported allergies and complications such as urticaria, eczema, swelling, and necrosis. People who have metal implants may feel colder around the implant site at low temperatures. This is because the skin of the body and the brain are susceptible to heat loss.
Do Titanium Implants Cause Cancer?
Before using titanium, cobalt-based aluminum had replaced mainly stainless steel and the primary material of permanent implants. This type of aluminum was resistant to corrosion, but due to the formation of a durable surface layer of chromium oxide, ion release was despite wear resistance. Because chromium, nickel, and cobalt are known to be carcinogenic, the entry of their ions into the body was a concern. The use of titanium is highly biocompatible and low risk. Another potential problem with residual titanium plates in the body is the entry of small scales from metal chips into the bloodstream, especially near the joints. In similar experiments, amounts of titanium and stainless steel were found in the joints, which was much lower in titanium implants. These particles are related to the points where the titanium is worn in contact with other surfaces.
The question is, can these particles lead to cancer? Studies in mice confirm that these particles are carcinogenic. Implant developers are well aware of these risks and have reduced concerns by increasing the durability and quality of metal implants in the body. However, the implants used in most of the world still have different quality and standards.
Do titanium implant plates stay healthy in the body?
There are various concerns about the titanium and metal plates used in the body, the durability of metal implants in the body, and their effect on the immune system. There is evidence that metals suppress the immune system as a whole. What happens if the immune system shuts down? Shutting down the immune system leads to infection. Some studies have shown that metal implants can increase white blood cells the lymphocyte reactivity. If lymphocytes develop, the implant may loosen or break. However, the incidence of this reaction is very low. Burning, pain, and infection are symptoms that should be removed when the implant is removed. Because it is often tough to neutralize a condition on organic material such as metal, ceramic, or plastic, removing the implant is the best chance of resolving the infection and other risks and problems. With the advancement of technology and industry in medicine, we are witnessing great news in implants and treatment of different parts of the body.
In Health News Center, in addition to the high quality of the products, we also paid attention to the implants' high durability because your health is important to us. You can see different types of orthopedic implants in the products section. Also, if you have any questions, ask in the comments. Our experts will surely answer you.