-
Category
Craniomaxillofacial Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Spine Surgery
Orthopedic Implants
Hip Surgery
Knee Surgery
Pectus Excavatum
Bone Graft
Disinfectants
Healthcare
12 Types of bump on the back of the head
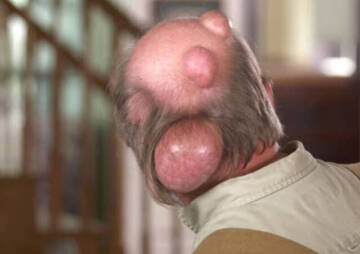
Bumps on any part of the head may be a concern, but in most cases, they are not serious. In this article, get acquainted with the important protrusions of the head area.
Bumps on any part of the head may be a concern, but in most cases, they are not serious. These bumps can be due to skin disease on the head, head injuries, infection, and abnormal growth of skull bone cells. Most of these problems are easily and spontaneously treated. However, in some cases it is necessary to see a doctor. What these bumps are and what kind of treatment they need is effective in removing them. That is why knowing them is so important.
Types of skull protrusions based on characteristics
The bumps on the back have certain characteristics according to which they are classified.
They may have the following characteristics:
- Big or small
- Soft or hard
- Single or multiple

- Fixed or movable
- Inflamed or non-inflamed
Each of these masses is created for reasons that in many cases are not a cause for concern. But as a rule, if a lump or wound suddenly formed in the head that was painful or deformed in appearance; You need to see a doctor to treat it.
Types of bump on the back of the head based on the causes
Masses on the back of the head can occur for a variety of reasons, sometimes accompanied by pain and sometimes deformity of the scalp. Some of the reasons are given below.
1. Mass due to head injury
If, for any reason, the back of the blow is struck, a slightly stiff mass and bleeding (hematoma) may develop at the site of the blow and under the skin. These bumps usually heal gradually over two weeks.
Cold compresses can be used to reduce swelling in minor injuries. The use of painkillers is also a great help to reduce pain.
But in cases of severe trauma, the person may suffer a concussion. Symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, extreme tiredness or drowsiness, and memory loss are important and should be treated by a physician.
2. Sebaceous cyst
Sebaceous cyst is a main group of cysts that are classified into two types.

Epidermal cyst
Epidermal cysts are made up of creatine and fat and affect the thin, outer layer of skin called the epidermis. These cysts may be the result of mild skin damage or acne and have certain symptoms.
- They are round cysts that grow slowly up to about five centimeters.
- Cysts are not painful unless they are infected.
- They are not cancerous
- They usually do not need treatment and go away on their own.
- If treatment is needed, antibiotics, steroid injections, or cyst drainage can be treated by a doctor.
Pilar cyst
Pilar cysts are made up of creatine and are present in the outer hair follicle or hair follicle. These cysts form around the front and back of the hairline. They are between half and five centimeters in diameter and usually they:

- They are non-cancerous.
- Are hereditary.
- It is more common in women than men.
- In most cases, they go away without treatment.
- Antibiotics are prescribed or the cyst is drained if needed.
3. Folliculitis
Inflammation of the hair follicles or folliculitis forms as prominent red or white lumps around the hair follicle. This lesion is more common in the head, especially in the back of the head. Folliculitis can be caused by a bacterial, fungal, viral infection, or inflammation of the skin during hair growth. People with diabetes are highly prone to inflammation of the hair follicles.
Bacteria can infect hair follicles and lead to folliculitis.
Treatment for folliculitis varies depending on what caused it. Antibiotics, antifungals and a proper diet are effective in improving it. In addition, when treating this mass, the head should not sweat as much as possible and hair creams and shampoos should not be used.

4. Pilomatrixoma
Pilomatrixoma is the name of a hair follicle tumor that is abnormal but usually harmless. This mass is caused by the overproduction of hair matrix cells.
Pilomatrixoma appears as dome-like lesions that are monochromatic or purple in color and can grow up to several centimeters. This mass is one of the most common types of bumps on the back of the head and neck and occurs in both children and adults.
To treat a hair follicle tumor, a sample is taken and then the mass is completely removed by outpatient surgery.

5. Lipoma
Lipoma is a soft mass of fat under the skin that moves in place. This mass grows slowly up to two centimeters. Lipoma is a harmless mass that can be found on different parts of the body. Of course, it appears less on the back of the head and neck.
Doctors do not know the exact cause of lipoma, but in many cases it occurs in people aged 40 to 60 years. It is slightly more common in men than women.
Lipomas do not need special treatment and go away on their own, but if they grow or harden, they need to be checked by a doctor.

6. Seborrheic keratosis
Seborrheic keratoses are wart-like, non-cancerous bumps that commonly appear on the head and neck of the elderly. These bumps are often harmless and therefore rarely treated. If the doctor is concerned about the cancerous appearance of these lumps, he will remove it using the method of cryotherapy or electrical surgery.

7. Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node swelling or lymphadenopathy occurs when the lymph node behind the ear becomes inflamed by external factors. Skin or ear infections are a major cause of swelling in these nodules. These swellings usually go away on their own, but if the swelling lasts for more than two weeks, you need to see a doctor.

8. Mastoiditis
The part of the skull bone behind the ear is called the mastoid. If bacteria infect this area of the skull, it can cause mastoiditis. This infection occurs in the air spaces of the bone.
Mastoiditis is more common in children than adults and is a serious infection that requires timely medical treatment. The disease manifests itself in the form of soft, red bumps on the back of the ear that may cause the ear to be pushed out.
Other symptoms include mastoiditis. For example, ear discharge, possible hearing loss, high fever, feeling sick and irritable, and headache
Doctors prescribe antibiotics to treat mastoiditis, and sometimes surgery is needed to open the mass and drain the infection.

9. Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis means premature healing of a skull joint. It is a congenital defect in which one or more fibrous joints between the bones of the baby's skull fuse prematurely. In this case, the baby's umbilical cord is formed when brain development is not yet complete. Because the baby's brain is still growing but the skull is closed, pressure is applied to the skull bone and the skull is deformed.
To treat craniosynostosis and correct the deformity of the head, surgery is needed so that the brain can grow normally. Early diagnosis and treatment create enough space for the brain to develop.

10. Masses caused by bone growth
Bone growth (exostosis) is a benign bone tumor that is rarely seen in the skull. This complication is caused by prolonged irritation, arthritis, infection, or trauma and is sometimes accompanied by chronic pain. For the treatment of this type of mass, painkillers, physiotherapy and surgery are the best choices.
11. Cranial bone tumor
Sometimes lumps on the back can be caused by a bone tumor. One of the most common types of cranial cancer is chordoma. This tumor grows from the bones at the base of the skull.

If the cordoma is small, it has no obvious symptoms, but if it is large, it is accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty walking and balance, headache, hearing problems and vision problems. In some cases, the tumor may spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment for cranial bone tumors will depend on a number of factors, including whether the tumor is benign or cancerous, the size of the tumor, the location of the tumor cells, and other individual variables.
12. Masses caused by subcutaneous hair
Sometimes hair grows into the skin as it grows. In this case, a small, firm red bump appears on the surface of the skin. This prominent mass is caused by pus from subcutaneous hair growth. Pimples are usually harmless and go away with hair growth. In some cases, it needs to be removed from under the skin with a special hair tool.

Types of bump on the back of the head due to the importance of treatment
Masses on the back of the head can be harmless or need treatment.
- Tumors that are not serious : A small bump on the scalp that goes away on its own is not serious.
- Masses that are relatively serious : Large swellings on the back of the head that are accompanied by redness or pain need to see a doctor, especially if they are accompanied by fever.
- Masses that are very important to treat : Scalp masses that grow and become fixed in place are very serious and definitely need treatment.
Not all bumps on the back of the head are abnormal
It is very common to find swelling and bulging behind. Masses form on the skin, under the skin, or in the bones. There are a wide range of reasons for these bumps. From trauma to congenital diseases such as craniosynostosis. But in addition to these cases, the human skull also has natural bumps on the back. This bulge, called the inion, is located at the bottom of the skull and at the junction with the neck muscle.
But if you feel any unusual bumps on the back that are growing and you feel pain and fever, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Do you have a bump behind your head or on your skull? Comment your questions below, we answer all them.